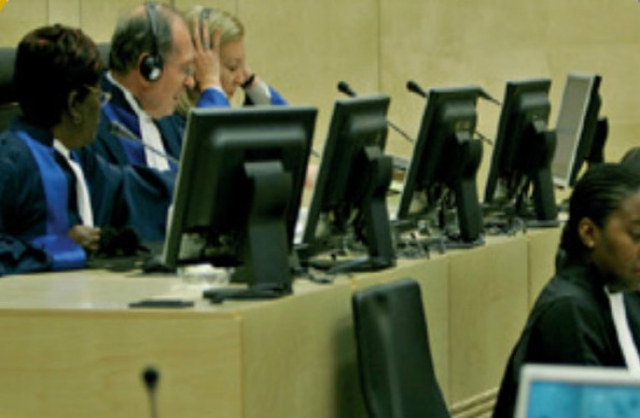
Photo: ICC court. The African Union will host a meeting in Ethiopia on October 12th to discuss a proposal for African countries to jointly withdraw from the International Criminal Court. ( © ICC/Associated Press )
Photo: ICC court. The African Union will host a meeting in Ethiopia on October 12th to discuss a proposal for African countries to jointly withdraw from the International Criminal Court. ( © ICC/Associated Press )
Tadias Magazine
By Tadias Staff
Published: Friday, October 4th, 2013
New York (TADIAS) – When Ghanian Judge Akua Kuenheyia, Vice-President of the International Criminal Court since 2003, spoke last November at Duke University about ICC and its impact on law and democracy in Africa, she could not have imagined that less than a year later a group of African politicians would stage a threat of mass withdrawal from the court in protest that the majority of those listed in the dockets hail from the continent. Some heads of state have even gone as far as describing the court as being on a “racist” witch hunt against black people.
A quick review of the 20 cases in 8 situations that have been brought before the International Criminal Court since its inception ten years ago on March 11th, 2003 indeed reveal that most of the indictments stem from the African continent — including the senseless violence that took place in Darfur, Sudan; Libya, Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Mali and the 2007-08 post-election violence in Kenya. One of the most notorious fugitives on the list include Joseph Kony of Uganda, who is wanted on multiple counts of crimes against humanity in regards to his role as the head of the Lord’s Resistance Army (LRA) that is accused of mass killing, torture and enslavement of people including children. The current President of Sudan, Lieutenant General Omar Hassan Ahmad Al-Bashir, was also indicted on March 4th, 2009 on five counts of crimes against humanity and two counts of war crimes for his parts related to the Darfur conflict.
It’s fair to note, however, that the ICC, which is an independent entity financed by member states and voluntary contributions, came to existence in the past decade on the heels of the Rwandan genocide that in the mid-nineties had taken the lives of more than half a million people in a matter of 100 days. In its recent compilation of frequently asked questions about the legal institution, the Council on Foreign Relations highlights that the International Criminal Court is based on a principle of complementarity: “This means that the ICC can only act when a national court is unable or unwilling to carry out a prosecution itself because the ICC was not created to supplant the authority of the national courts. However, when a state’s legal system collapses or when a government is a perpetrator of heinous crimes, the ICC can exercise jurisdiction.”
Furthermore, based on the statute established at the United Nations conference in Rome on July 17, 1998, the prosecutor “can initiate an investigation on the basis of a referral from any State Party or from the United Nations Security Council. In addition, the Prosecutor can initiate investigations proprio motu on the basis of information on crimes within the jurisdiction of the Court received from individuals or organizations (“communications”).”
Below is a list of pending cases before the international court courtesy of ICC.
Situation in Uganda
The case The Prosecutor v. Joseph Kony, Vincent Otti, Okot Odhiambo and Dominic Ongwen is currently being heard before Pre-Trial Chamber II. In this case, five warrants of arrest have been issued against [the] five top members of the Lords Resistance Army (LRA). Following the confirmation of the death of Mr Lukwiya, the proceedings against him have been terminated. The four remaining suspects are still at large.
Situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
In this situation, five cases have been brought before the relevant Chambers: The Prosecutor v. Thomas Lubanga Dyilo; The Prosecutor v. Bosco Ntaganda; The Prosecutor v. Germain Katanga; The Prosecutor v. Mathieu Ngudjolo Chui; The Prosecutor v. Callixte Mbarushimana; and The Prosecutor v. Sylvestre Mudacumura. Thomas Lubanga Dyilo, Germain Katanga and Bosco Ntaganda are currently in the custody of the ICC. Sylvestre Mudacumura remains at large.
Trial Chamber I convicted Mr Lubanga Dyilo on 14 March 2012. The trial in this case, The Prosecutor v. Thomas Lubanga Dyilo, had started on 26 January 2009. On 10 July 2012, he was sentenced to a total period of 14 years of imprisonment. The time he spent in the ICC’s custody will be deducted from this total sentence. On 7 August 2012, Trial Chamber I issued a decision on the principles and the process to be implemented for reparations to victims in the case. All three decisions are currently subject to appeal.
The trial in the case of The Prosecutor v. Germain Katanga and Mathieu Ngudjolo Chui started on 24 November 2009. Closing statements in the case were heard from 15 to 23 May 2012. On 21 November 2012, Trial Chamber II decided to sever the charges against Mathieu Ngudjolo Chui and Germain Katanga. On 18 December 2012, Trial Chamber II acquitted Mathieu Ngudjolo Chui of the charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity and ordered his immediate release. On 21 December 2012, Mathieu Ngudjolo Chui was released from custody. The Office of the Prosecutor has appealed the verdict.
The verdict regarding German Katanga will be delivered at a later stage.
The confirmation of charges hearing in the case The Prosecutor v. Callixte Mbarushimana took place from 16 to 21 September 2011. On 16 December 2011, Pre-Trial Chamber I decided by Majority to decline to confirm the charges against Mr Mbarushimana. Mr Mbarushimana was released from the ICC’s custody on 23 December 2011, upon the completion of the necessary arrangements, as ordered by Pre-Trial Chamber I.
On 22 March 2013, Bosco Ntaganda surrendered himself voluntarily and is now in the ICC’s custody. His initial appearance hearing took place before Pre-Trial Chamber II on 26 March 2013. The confirmation of charges hearing in the case is scheduled to start on 10 February 2014.
Situation in Darfur, Sudan
There are five cases in the situation in Darfur, Sudan: The Prosecutor v. Ahmad Muhammad Harun (”Ahmad Harun”) and Ali Muhammad Ali Abd-Al-Rahman (“Ali Kushayb”); The Prosecutor v. Omar Hassan Ahmad Al Bashir; The Prosecutor v. Bahar Idriss Abu Garda; The Prosecutor v. Abdallah Banda Abakaer Nourain and Saleh Mohammed Jerbo Jamus; and The Prosecutor v. Abdel Raheem Muhammad Hussein.
Warrants of arrest have been issued by Pre-Trial Chamber I for Messrs Harun, Kushayb, Al Bashir and Hussein. The four suspects remain at large.
A summons to appear was issued for Mr Abu Garda, who appeared voluntarily before the Chamber on 18 May 2009. After the hearing of confirmation of charges, on February 2010, Pre-Trial Chamber I declined to confirm the charges. Mr Abu Garda is not in the custody of the ICC.
Two other summonses to appear were issued for Mr Banda and Mr Jerbo who appeared voluntarily on 17 June 2010; the confirmation of charges hearing took place on 8 December 2010. On 7 March 2011, Pre- Trial Chamber I unanimously decided to confirm the charges of war crimes brought by the ICC’s Prosecutor against Mr Banda and Mr Jerbo, and committed them to trial. The trial in the case The Prosecutor v. Abdallah Banda Abakaer Nourain and Saleh Mohammed Jerbo Jamus is scheduled to start on 5 May 2014.
Situation in the Central African Republic
The situation was referred to the Court by the Government of the Central African Republic in December 2004. The Prosecutor opened an investigation in May 2007. In the only case in this situation, The Prosecutor v. Jean-Pierre Bemba Gombo, Pre-Trial Chamber II confirmed, on 15 June 2009, two charges of crimes against humanity and three charges of war crimes, and committed the accused to trial before Trial Chamber III. The trial started on 22 November 2010.
Situation in the Republic of Kenya
On 31 March 2010, Pre-Trial Chamber II granted the Prosecutor’s request to open an investigation proprio motu in the situation in Kenya, State Party since 2005. Following summonses to appear issued on 8 March 2011, six Kenyan citizens voluntarily appeared before Pre-Trial Chamber II on 7 and 8 April 2011. The confirmation of charges hearing in the case The Prosecutor v. William Samoei Ruto and Joshua Arap Sang were held from 1 to 8 September 2011. The confirmation of charges hearing in the case The Prosecutor v. Uhuru Muigai Kenyatta took place from 21 September to 5 October 2011. On 23 January 2012, the judges declined to confirm the charges against Henry Kiprono Kosgey and Mohammed Hussein Ali. Pre-Trial Chamber II confirmed the charges against William Samoei Ruto, Joshua Arap Sang, Francis Kirimi Muthaura and Uhuru Muigai Kenyatta and committed them to trial. On 18 March 2013, the charges against Francis Kirimi Muthaura were withdrawn. The trial of William Samoei Ruto and Joshua Arap is started on 10 September 2013 and the trial of Uhuru Muigai Kenyatta is scheduled to start on 12 November 2013.
On 2 October 2013, Pre-Trial Chamber II unsealed an arrest warrant against Walter Osapiri Barasa, initially issued on 2 August 2013, for several offences against the administration of justice consisting in corruptly or attempting to corruptly influencing ICC witnesses.
Situation in Libya
On 26 February 2011, the United Nations Security Council decided unanimously to refer the situation in Libya since 15 February 2011 to the ICC Prosecutor. On 3 March 2011, the ICC Prosecutor announced his decision to open an investigation in the situation in Libya, which was assigned by the Presidency to Pre-Trial Chamber I. On 27 June 2011, Pre-Trial Chamber I issued three warrants of arrest respectively for Muammar Mohammed Abu Minyar Gaddafi, Saif Al-Islam Gaddafi and Abdullah Al-Senussi for crimes against humanity (murder and persecution) allegedly committed across Libya from 15 until at least 28 February 2011, through the State apparatus and Security Forces. On 22 November 2011, Pre-Trial Chamber I formally terminated the case against Muammar Gaddafi due to his death. The two other suspects are not in the custody of the Court. On 31 May 2013, Pre-Trial Chamber I rejected Libya’s challenge to the admissibility of the case against Saif Al Islam Gaddafi and reminded Libya of its obligation to surrender the suspect to the Court.
Situation in Côte d’Ivoire
Côte d’Ivoire, was not party to the Rome Statute at the time, had accepted the jurisdiction of the ICC on 18 April 2003; more recently, and on both 14 December 2010 and 3 May 2011, the Presidency of Côte d’Ivoire reconfirmed the country’s acceptance of this jurisdiction. On 15 February 2013, Côte d’Ivoire ratified the Rome Statute.
On 3 October 2011, Pre-Trial Chamber III granted the Prosecutor’s request for authorisation to open investigations proprio motu into the situation in Côte d’Ivoire with respect to alleged crimes within the jurisdiction of the Court, committed since 28 November 2010, as well as with regard to crimes that may be committed in the future in the context of this situation. On 22 February 2012, Pre-Trial Chamber III decided to expand its authorisation for the investigation in Côte d’Ivoire to include crimes within the jurisdiction of the Court allegedly committed between 19 September 2002 and 28 November 2010.
On 23 November 2011, Pre-Trial Chamber III issued a warrant of arrest under seal in the case The Prosecutor v. Laurent Gbagbo for four counts of crimes against humanity. The arrest warrant against Mr Gbagbo was unsealed on 30 November 2011, when the suspect was transferred to the ICC detention centre at The Hague, by the Ivorian authorities. On 5 December 2011, Pre-Trial Chamber III held an initial appearance hearing. The confirmation of charges hearing took place between 19 and 28 February 2013. On 3 June 2013, Pre-Trial Chamber I adjourned the hearing on the confirmation of charges and requested the Prosecutor to consider providing further evidence or conducting further investigation with respect to the charges presented against Laurent Gbagbo.
On 22 November 2012, Pre-Trial Chamber I decided to unseal a warrant of arrest issued initially on 29 February 2012 against Simone Gbagbo for four counts of crimes against humanity allegedly committed in the territory of Côte d’Ivoire between 16 December 2010 and 12 April 2011. Mrs. Gbagbo is not in the custody of the Court.
On 30 September 2013, Pre-Trial Chamber I unsealed an arrest warrant against Charles Blé Goudé initially issued on 21 December 2011 for four counts of crimes against humanity allegedly committed in the territory of Côte d’Ivoire between 16 December 2010 and 12 April 2011. Mr Blé Goudé is not in the custody of the Court.
Situation in Mali
On 16 January 2013, the Office of the Prosecutor opened an investigation into alleged crimes committed on the territory of Mali since January 2012.
The situation in Mali was referred to the Court by the Government of Mali on 13 July 2012. After conducting a preliminary examination of the situation, including an assessment of admissibility of potential cases, the OTP determined that there was a reasonable basis to proceed with an investigation.
The situation in Mali is assigned to Pre-Trial Chamber II.
—
Related:
Kofi Annan Urges African Leaders to Stand by International Criminal Court (LA Times)
Ethiopia Criticises ICC Policy against Africa (Sudan Tribune)
African Leaders to Hold Summit in Ethiopia on Kenya’s International Court Cases (VOA)
Ethiopia Supports Campaign Against International Court (VOA News)
Join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.