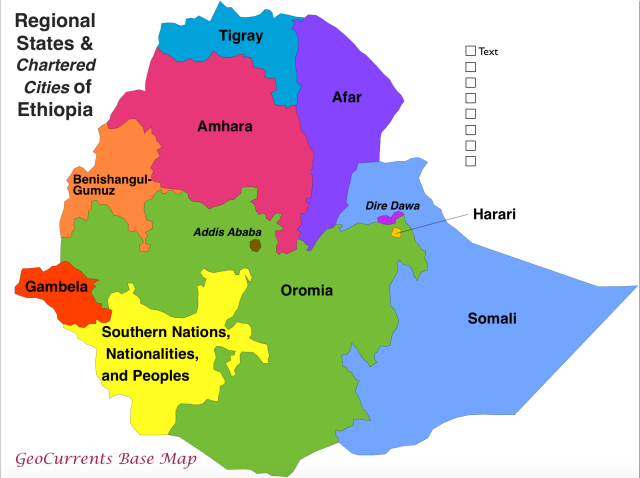
 Unlike Ethiopia's ethnofederalism where a state is defined according to ethnicity (see Oromia, Amhara, Tigray, Gambela, Somali, etc), a federal system in other diverse countries, such as the U.S., is simply a constitutional power-sharing arrangement between a central government and the population it serves regardless of group identity and with a purpose of promoting a common national and cultural tradition. (Image: GeoCurrents Maps of Ethiopia)
Unlike Ethiopia's ethnofederalism where a state is defined according to ethnicity (see Oromia, Amhara, Tigray, Gambela, Somali, etc), a federal system in other diverse countries, such as the U.S., is simply a constitutional power-sharing arrangement between a central government and the population it serves regardless of group identity and with a purpose of promoting a common national and cultural tradition. (Image: GeoCurrents Maps of Ethiopia)
What is a Federal Government? – Definition, Powers & Benefits
A federal government is a system that divides up power between a strong national government and smaller local governments. We’ll take a look at how power plays out between the national and local government, and the benefits of a federal government.
Benefits of A Federal Government
Why does the United States have a federal government but not Great Britain? The answer has to do with size. Federal governments are best used in large countries where there exists a diverse group of people with diverse needs but a common culture that unites them together.
For example, think of the difference between Wyoming (the least densely populated state) and New Jersey (the most densely populated state). Clearly, the needs at the local level of each state will be different, so they should have different local governments to address those needs. Nonetheless, both states share a common culture and interest and, therefore, are united by the national government.
Federal governments help address the wide variety of needs of a geographically large country. It is no wonder, then, that federal governments exist in large countries, like the United States, Mexico, Germany, Canada, Australia, Brazil, and others.
Federal Government in the United States: Division of Power
In the United States, the Constitution created the federal system by limiting the activities of the national government to a few areas, such as collecting taxes, providing for defense, borrowing money on credit, regulating commerce, creating a currency, establishing post offices and post roads, granting patents, creating lower courts, and declaring war. The 10th amendment of the Constitution, on the other hand, gave all other powers to the states. As a result, any specific power not given to the Federal government is a power of the state government.
In theory, the United States federal system has a clear division between what states oversee and what the federal government oversees.
—
Related:
Ethiopian Federal System – What Is in It? (AllAfrica.com)
Join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.